Professional Cockroach Control Services
Professional Cockroach Control Services
With over 4,600 different species worldwide, cockroaches are among the most resilient and adaptable pests on the planet. While most prefer warm, humid environments, about 30 species, including German, American, and Oriental cockroaches, commonly invade homes. Our professional cockroach control services provide targeted solutions to eliminate these persistent pests from your home and prevent future infestations.
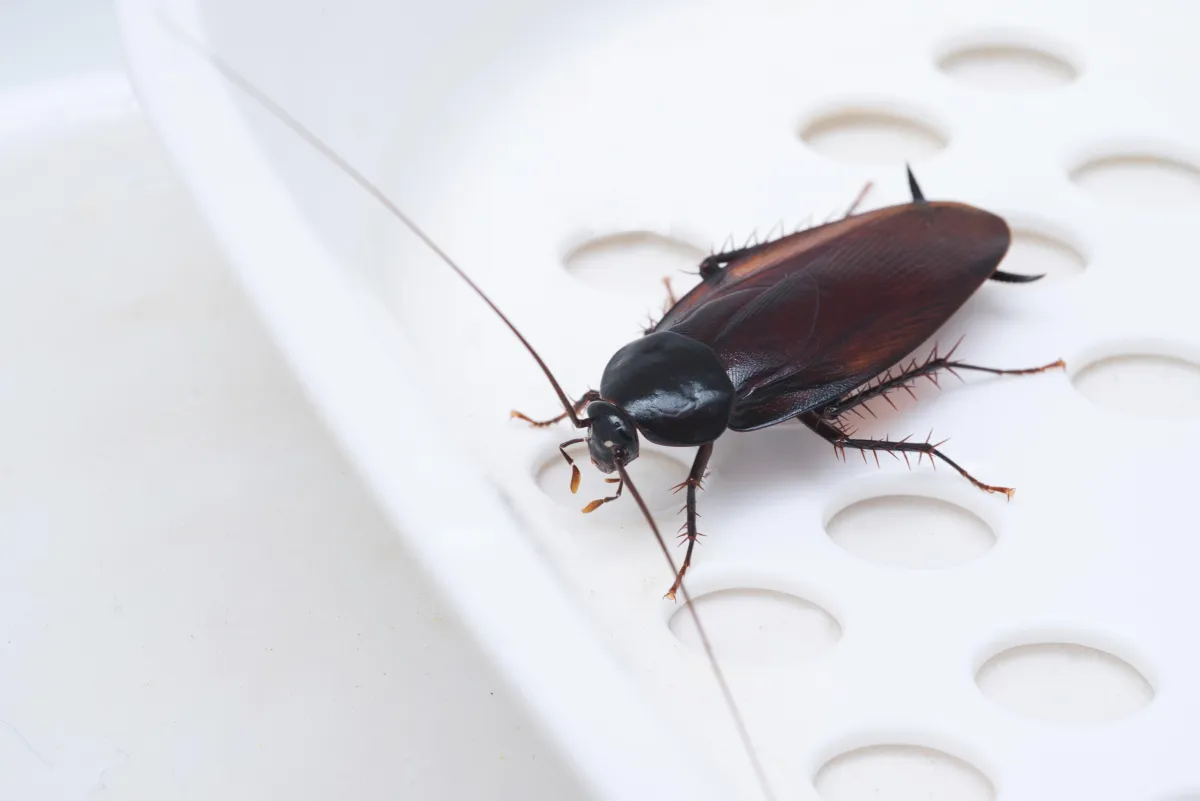


Understanding Cockroaches
What Are Cockroaches?
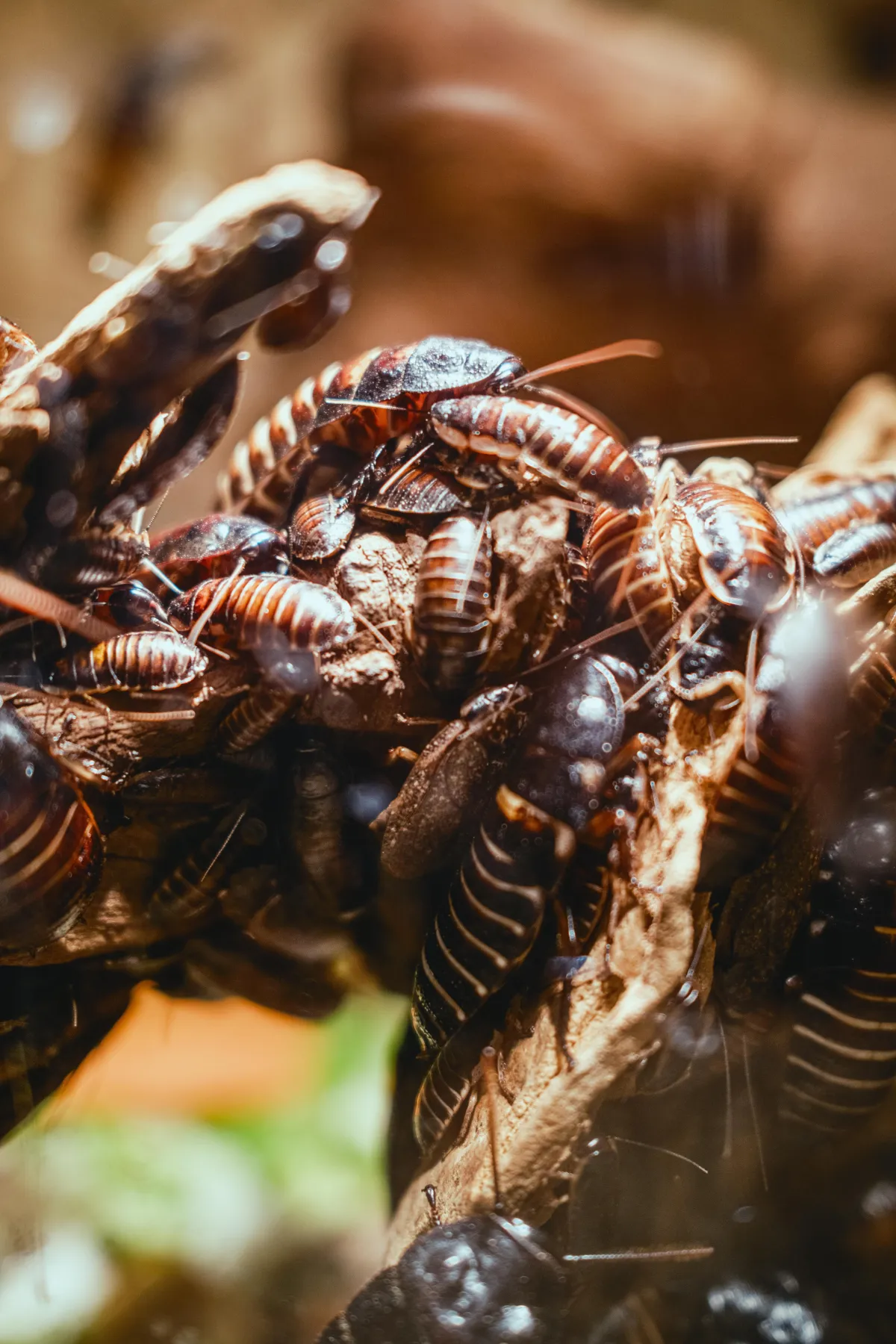

Cockroaches are insects belonging to the order Blattodea, dating back over 300 million years, making them one of the most ancient and resilient pests. These nocturnal insects have flat, oval bodies and are notorious for their ability to survive in almost any environment that provides food, water, and shelter, including human habitations.
Cockroach Characteristics
Appearance: Flat, oval-shaped bodies with long antennae and spiny legs
Size: Range from 1/2 inch to over 2 inches in length depending on species
Body Structure: No true colonies, but gather in large numbers where conditions are favorable
Lifespan: Complete metamorphosis with three stages: egg, nymph, and adult
Diet: Omnivorous scavengers that consume almost anything organic, including food scraps, paper, glue, and fabrics
Common Household Cockroach Species
Several factors can make your home attractive to cockroaches:


German Cockroach
Size: 1/2 to 5/8 inch long
Color: Light brown with two dark parallel stripes on the pronotum
Damage: Most common indoor species, reproduces rapidly
Concern: Can complete their lifecycle entirely indoors and spread disease-causing organisms
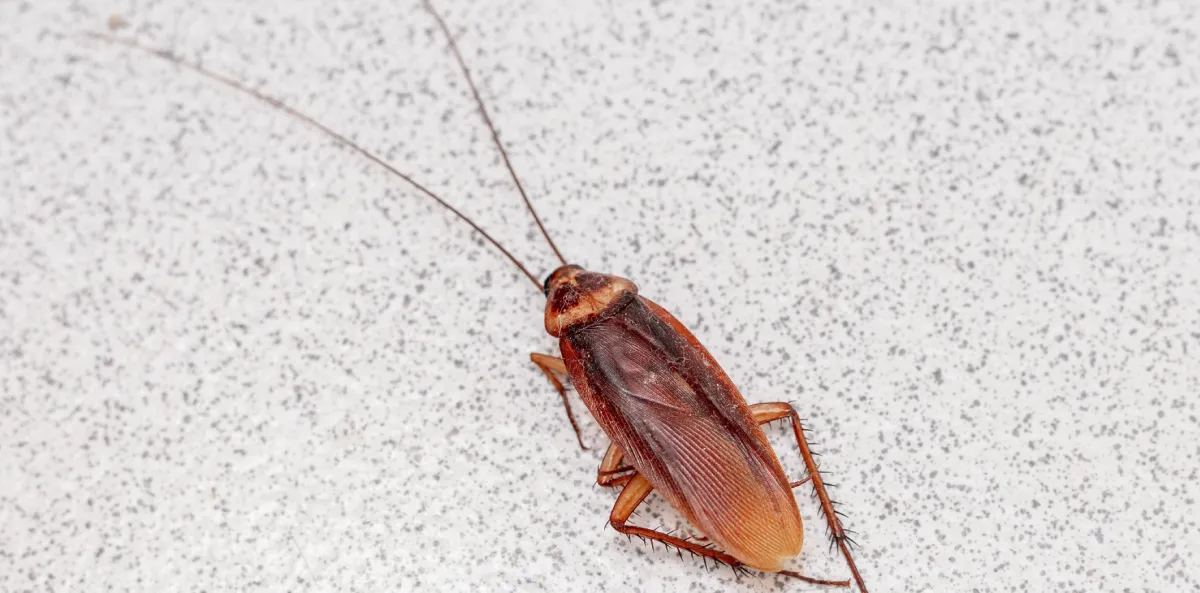


American Cockroach
Size: 1-1/2 to 2 inches long
Color: Reddish-brown with a yellowish figure-8 pattern on the head
Damage: Prefers warm, moist areas like basements and sewers
Concern: Can contaminate food and surfaces with bacteria and pathogens


Garden Millipede
Size: About 1 inch long
Color: Dark brown to black, glossy appearance
Damage: Often found in damp areas like basements and drains
Concern: Emits a strong, unpleasant odor and can trigger allergic reactions

Signs of a Cockroach Infestation
You may have a cockroach problem if you notice:


Image Live Cockroaches:
Adult cockroaches visible in the home, especially at night

Image Droppings:
Small black pellets resembling coffee grounds or pepper

Image Egg Cases:
Brown, purse-shaped egg capsules (oothecae) in hidden areas

Image Smear Marks:
Dark, irregular streaks along walls and baseboards where cockroaches travel

Image Shed Skins
Translucent molted skins left behind as nymphs grow
Hidden Indications
Musty Odor:
Distinctive unpleasant smell in areas where cockroaches congregate
Contaminated Food:
Unusual food package damage or contamination
Nighttime Activity:
More cockroach sightings when lights are turned on at night
Allergic Reactions:
Unexplained respiratory symptoms or skin rashes, especially in children

The Risks of Cockroach Infestations
Cockroaches can cause several problems in your home:


Image Disease Transmission:
Cockroaches can carry and spread pathogens including E. coli and Salmonella

Image Allergen Production:
Their shed skins and droppings can trigger allergies and asthma in sensitive individuals

Image Food Contamination:
They leave behind droppings, regurgitated fluid, and bacteria on surfaces

Image Property Damage:
Large infestations can damage books, papers, and even electronic equipment

Image Psychological Distress:
Their presence can cause significant anxiety and embarrassment

Our Comprehensive Cockroach Control Approach
We take a multi-faceted approach to cockroach control:

Thorough Inspection
Our technicians will conduct a detailed inspection to: Identify the specific cockroach species present
Locate hiding spots, breeding areas, and entry points
Determine the extent of the infestation
Identify contributing factors that may be enabling the infestation


Customized Treatment Plan
Based on our findings, we'll develop a tailored cockroach control strategy that may include:
Targeted Baiting
Gel baits placed in cracks and crevices where cockroaches hide
Granular baits for less accessible areas
Bait rotation to prevent resistance development
Residual Treatments
Crack and crevice applications in key areas
Barrier treatments to prevent new cockroaches from entering
Focused applications in kitchens, bathrooms, and other vulnerable areas
Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs)
Specialized products that disrupt the cockroach life cycle
Prevents immature cockroaches from developing into reproductive adults
Provides long-term population control

Prevention Strategies
We'll help prevent future cockroach problems by: Identifying and sealing entry points
Recommending moisture control solutions
Suggesting proper food storage and waste management practices
Advising on regular cleaning and maintenance routines
Follow-Up Protection
Our commitment to cockroach control includes: Scheduled follow-up visits to ensure complete elimination:
Monitoring for new activity
Additional treatments as needed
Continuous protection against future infestations

Cockroach Prevention Tips
To help keep cockroaches away from your home:
Kitchen Management
Store food in airtight containers
Clean up spills and crumbs promptly
Empty garbage regularly and keep bins clean
Wash dishes promptly rather than leaving them in the sink
Moisture Control
Fix leaky pipes and faucets
Use dehumidifiers in damp areas
Ensure proper ventilation in bathrooms and kitchens
Check for and repair water damage
Home Maintenance
Seal cracks and crevices in walls, baseboards, and around pipes
Repair torn window screens and door sweeps
Declutter to eliminate hiding spots
Vacuum regularly, especially in hard-to-reach areas

The Risks of Cockroach Infestations
Cockroaches can cause several problems in your home:

Health Concerns
Disease Transmission: Cockroaches carry bacteria that can cause food poisoning and other illnesses
Allergic Reactions: Their saliva, droppings, and shed skins contain powerful allergens that can trigger asthma attacks
Contamination: They contaminate food and surfaces with pathogens as they feed and move around

Property Issues
Food Spoilage: They contaminate and damage stored food products
Odor Problems: Large infestations create a distinctive unpleasant odor that permeates the home
Psychological Distress: The presence of cockroaches can cause anxiety and discomfort
Our Cockroach Control Guarantee
We stand behind our services with our satisfaction guarantee. If cockroaches return between scheduled treatments, so will we—at no additional cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Get answers to common questions about cockroaches
Do cockroaches bite?
While cockroaches are not typically aggressive toward humans, they can bite in rare instances, usually when populations are extremely high and food is scarce. Their bites can cause minor wounds and potential irritation, but this behavior is uncommon.
How quickly do cockroaches multiply?
Cockroaches reproduce extremely rapidly. A single German cockroach female can produce up to 400 offspring in her lifetime, with eggs hatching in as little as 28 days. Their rapid reproduction rate makes prompt control essential to prevent major infestations.
Where do cockroaches live?
Cockroaches prefer to live near reliable water sources in moist, humid, dark spaces. They are commonly found in kitchens and bathrooms, hiding in cupboards, drains, under appliances, in ceilings, cellars, and wall cracks. Being nocturnal, they typically emerge at night to search for food.
What attracts cockroaches?
Cockroaches are attracted to food residues, garbage, pet food, and moisture. They thrive in warm, damp environments with easy access to food and water. Poor sanitation, unsealed food, crumbs, structural deficiencies, and high humidity levels in kitchens, bathrooms, and basements create ideal conditions for cockroach infestations.
How do I get rid of cockroaches?
To get rid of cockroaches, maintain good sanitation practices by keeping food sealed and cleaning up spills promptly. Use baits, traps, and appropriate insecticides in high-activity areas. Seal entry points, reduce moisture by fixing leaks, remove hiding spots, and store food properly. For severe infestations, professional pest control services provide the most effective and lasting solution.
Ready for Cockroach-Free Living?
Don't let cockroaches threaten your family's health and peace of mind. Our professional cockroach control services provide effective, lasting solutions to eliminate these persistent pests. 100% Satisfaction Guarantee Licensed & Insured Technicians Same-Day Service Available
Or call us directly
(866) 555-7890
We guarantee your satisfaction, if cockroaches return between scheduled treatments, so will we at no additional cost

© Copyright 2025. [Lead Machine: Pest Control Snapshot]. All Rights Reserved.