Professional Earwig Control Services
Professional Earwig Control Services
With over 2,000 different species worldwide, earwigs are easily recognized by their distinctive pincers or forceps at the end of their abdomen. While most earwigs live outdoors beneath leaves and in areas with mulch, they can invade homes seeking moisture and shelter, especially during inclement weather. Our professional earwig control services provide targeted solutions to eliminate these pests from your home and prevent future infestations.


Understanding Earwigs
What Are Earwigs?

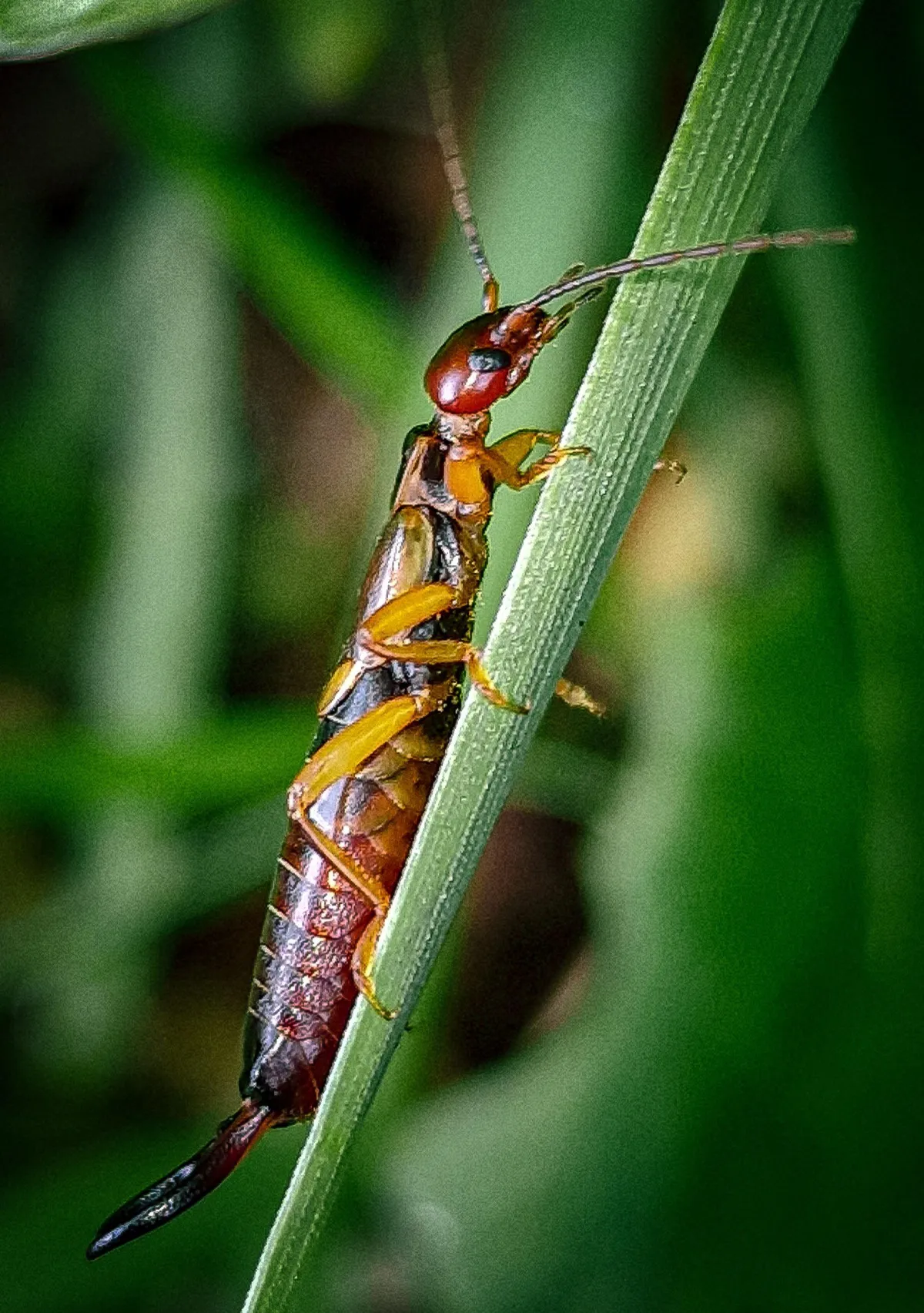
Earwigs are insects belonging to one of the smaller insect orders. Most people recognize earwigs by their forceps pincers or cerci, which are connected to the earwig's abdomen. Contrary to old superstitions, earwigs do not crawl into people's ears to feed. They are primarily outdoor insects that occasionally enter homes in search of moisture and dark environments when conditions outside become unfavorable.
Earwig Characteristics:
Appearance: Elongated, flattened bodies with prominent pincers (forceps) at the rear end
Size: Range from 1/4 inch to 1 inch in length depending on species
Colony Structure: No true colonies, but may gather in damp areas in large numbers
Lifespan: Complete metamorphosis with three stages: egg, nymph, and adult
Diet: Omnivorous—most feed on decaying plant matter, but some species are predatory
Common Household Earwig Species
Several factors can make your home attractive to earwigs:
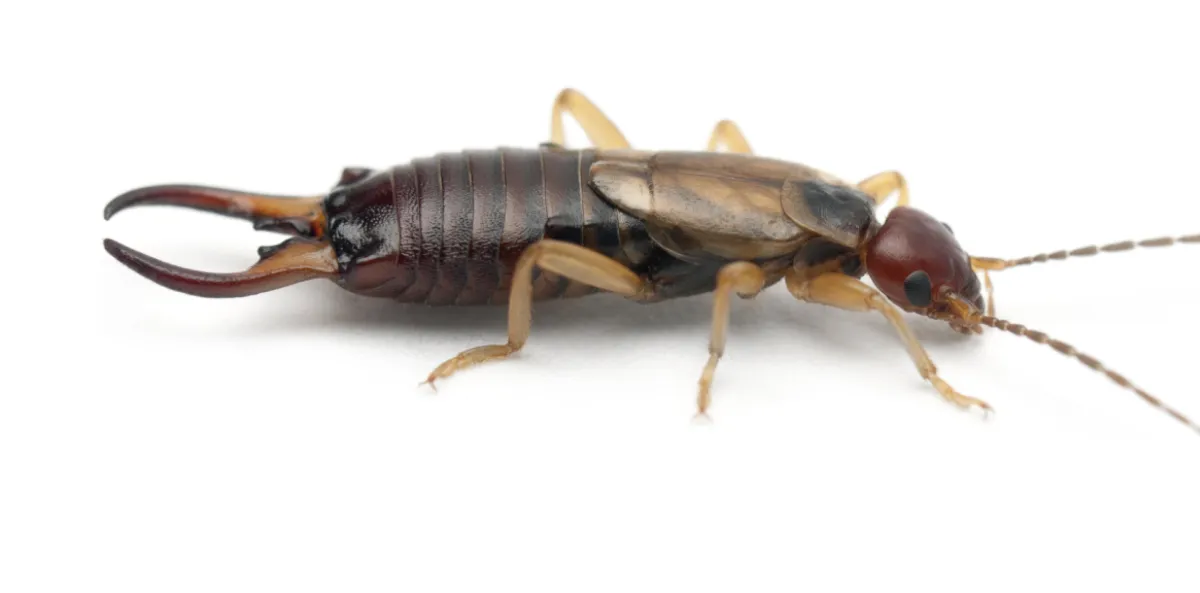


European Earwig
Size: 1/2 to 3/4 inch long
Color: Reddish-brown with pale yellow legs
Behavior: Most common household earwig, active at night, seeks damp locations
Concern: Can pinch if handled, though rarely breaks the skin or causes serious discomfort


Striped Earwig
Size: 1/2 to 1 inch long
Color: Brown with light stripes on the abdomen
Behavior: Often found in gardens and may enter homes during dry conditions
Concern: Larger pincers that can cause slight discomfort if handled


Ringlegged Earwig
Size: About 1/2 inch long
Color: Tan to dark brown with distinctive light rings on legs
Behavior: Prefers very moist environments like bathrooms and kitchens
Concern: Can damage houseplants if present in large numbers

Signs of an Earwig Infestation
You may have an earwig problem if you notice:


Image Live Earwigs:
Adult earwigs visible in damp areas of the home

Image Damage to Plants:
Small, irregular holes in houseplant leaves

Image Damp Areas:
Earwigs congregating in moist environments like bathrooms and basements

Image Nocturnal Activity:
More earwig sightings at night when they are most active

Image Mulch Proximity:
Earwigs near entry points close to outdoor mulch or leaf litter
Hidden Indications
Moisture Issues:
Damp areas in basements, bathrooms, or around foundations.
Cracks and Gaps:
Small openings near doors, windows, and foundation that allow entry
Weather Changes:
Increased earwig activity indoors during rainy periods or drought
Organic Debris:
Accumulation of leaves, mulch, or plant matter near home foundation

The Risks of Earwig Infestations
Earwigs can cause several problems in your home:


Being Pinched:
Earwigs can use their forceps to grasp onto a finger if agitated

Fast Reproduction:
Female earwigs lay 20-60 eggs at a time, with 2-6 rounds of eggs

Increased Presence:
Inclement weather drives more earwigs indoors seeking warmth and dryness

Plant Damage:
Some earwig species feed on and damage houseplants

Unsightly Nuisance:
Their presence can be disturbing to residents and guests

Our Comprehensive Earwig Control Approach
We take a multi-faceted approach to earwig control:

Thorough Inspection
Our technicians will conduct a detailed inspection to: Identify earwig activity and the severity of the infestation
Locate hiding spots, entry points, and moisture sources
Assess spots that attract dampness and moisture
Determine contributing factors that may be enabling the infestation


Customized Treatment Plan
Based on our findings, we'll develop a tailored earwig control strategy that may include:
For Interior Infestations
Targeted treatments for affected areas with active earwig populations
Crack and crevice applications in bathrooms, kitchens, and basements
Recommendations for reducing moisture that attracts earwigs
For Exterior Protection
Perimeter treatments to create a protective barrier
Applications to mulch beds and foundation areas
Management of vegetation and organic debris near the home
For Long-term Prevention
Scientifically proven customized treatment plan
Fortification against reinfestation
Guidance on moisture control and landscaping practices

Prevention Strategies
We'll help prevent future earwig problems by: Identifying and sealing entry points
Recommending dehumidifiers and moisture control solutions
Suggesting proper landscape maintenance to reduce earwig harborage
Advising on regular inspection and maintenance routines
Follow-Up Protection
Our commitment to earwig control includes:
Scheduled follow-up visits to ensure complete elimination
Monitoring for new activity
Additional treatments as needed
Continuous protection against future infestations

Earwig Prevention Tips
To help keep earwigs away from your home:
Moisture Control
Fix leaky pipes and faucets
Use dehumidifiers in damp areas
Ensure proper drainage around foundation
Ventilate crawl spaces and basements properly
Home Maintenance
Seal cracks and gaps in foundation and exterior walls
Install door sweeps and weather stripping
Remove organic debris from gutters and downspouts
Keep outdoor lights to a minimum as they attract earwigs
Yard Management
Keep mulch away from foundation walls
Remove leaf litter, fallen branches, and yard debris
Store firewood and other materials away from the home's exterior
Trim vegetation to reduce damp hiding places near the foundation

The Risks of Earwig Infestations
Earwigs can cause several problems in your home:

Nuisance Concerns
Unpleasant Presence: The sight of earwigs with their intimidating pincers can be disturbing
Rapid Increase: Their fast reproduction rate can lead to more significant infestations
Seasonal Invasions: Weather changes can drive large numbers indoors simultaneously

Property Considerations
Plant Damage: Some earwigs feed on and damage indoor and outdoor plants
Moisture Indication: Their presence often signals excess humidity or water issues
Entry Point Issues: Infestations may indicate cracks and gaps that need sealing
Our Earwig Control Guarantee
We stand behind our services with our satisfaction guarantee. If earwigs return between scheduled treatments, so will we—at no additional cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Get answers to common questions about earwigs
Do earwigs bite?
Earwigs don't actually bite. However, they do have forceps or pincers that they can use to grasp onto skin if disturbed, which may produce a mild pinch. This defensive reaction rarely breaks the skin or causes serious discomfort. The pincers on male earwigs are usually larger than those on females but both are generally harmless to humans.
Are earwigs dangerous?
Earwigs are not harmful to humans. They don't bite, sting, or carry diseases. The old superstition that earwigs crawl into people's ears is not true—they don't seek out human ears. While their appearance with the prominent pincers might seem intimidating, they pose no real threat to human health or safety and are generally considered a nuisance pest rather than a dangerous one.
What do earwigs eat?
Earwigs are omnivorous. Most species feed primarily on decaying plant matter and garden debris, though they may occasionally damage living plants by chewing small, irregular holes in leaves. Some earwig species are also skilled predators that feed on other insects, acting as beneficial garden pest controllers. Indoors, earwigs don't typically cause damage by feeding, as they're mostly searching for moisture and shelter rather than food.
Why are there earwigs in my house?
Earwigs enter homes seeking moisture and shelter, especially during weather changes. They are attracted to damp, dark environments such as basements, bathrooms, and kitchens. When outdoor conditions become too dry or too wet, earwigs may move indoors. Entry typically occurs through cracks in foundations, gaps around doors and windows, or other small openings. Areas with excessive moisture from leaks or high humidity are particularly attractive to these pests.
How do I get rid of earwigs in my home?
To get rid of earwigs in your home, start by reducing moisture by fixing leaks and using dehumidifiers. Seal cracks and gaps in walls, windows, and doors to prevent entry. Remove hiding places by decluttering and keeping areas clean and dry. Use traps in high-activity areas to capture earwigs. For persistent problems, professional pest control services provide the most effective and lasting solution with targeted treatments and preventative measures to keep earwigs from returning.
Ready for Earwig-Free Living?
Don't let earwigs make themselves at home in your damp spaces. Our professional earwig control services provide effective, lasting solutions to eliminate these pests. 100% Satisfaction Guarantee Licensed & Insured Technicians Same-Day Service Available
Or call us directly
(866) 555-7890
We guarantee your satisfaction—if earwigs return between scheduled treatments, so will we at no additional cost.

© Copyright 2025. [Lead Machine: Pest Control Snapshot]. All Rights Reserved.